parasternal heave - palpating for heaves and thrills : 2024-11-02 parasternal heave Learn how to perform cardiology examination by checking for parasternal heave and thrills, which are signs of cardiac enlargement. Watch a demonstration by . parasternal heave76 talking about this. Artisanal recipes & natural ingredients
High quality of malting barley is reflected by optimal protein content (9.5%~11.5%), higher β-amylase activity and grain weight. Grain protein content is .
parasternal heaveLearn how to perform a comprehensive cardiovascular examination, including vital signs, pulses, veins, chest, lung, and abdominal and extremity inspection and palpation. Find out how to measure blood . Learn how to detect a parasternal heave by placing the heel of the hand over the left parasternal region. A parasternal heave is caused by right ventricular . Left parasternal heave is a systolic elevation of left costal cartilages due to contraction of a hypertrophied right ventricle.In the early nineteen sixties,. Palpation and auscultation: A parasternal RV heave is often palpable at the left lower sternal border while the closure of the pulmonic valve (palpable P2) is approximately at the level of the left second . Learn how to detect a parasternal heave, a sign of right ventricular enlargement or severe left atrial enlargement. Find out the causes, annotations and . Parasternal heave is a sign of right ventricular strain and pulmonary hypertension in patients with pulmonary embolism (PE). Learn how to diagnose, risk stratify, and treat PE with anticoagulation, .Nov 20, 2022 — A sustained and prolonged left parasternal heave is indicative of right ventricular hypertrophy. Another physical finding observed in cardiomegaly is the holosystolic murmur of mitral or tricuspid .
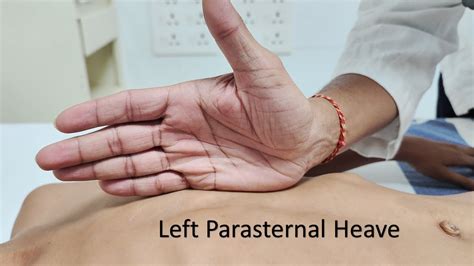
Jan 1, 2018 — A parasternal heave is detected by placing the heel of the hand over the left parasternal region. In the presence of a heave the heel of the hand is lifted off the chest wall with each systole. A parasternal heave is caused by: right ventricular enlargement, or; rarely, severe left atrial enlargement which pushes the right ventricle forwardsparasternal heave and loud P2, suggesting pulmonary hypertension as a cause. an enlarged, tender, pulsatile liver and, occasionally, mild jaundice. a pansystolic murmur at the left lower sternal edge that is increased by .Mar 28, 2020 — Left parasternal heave is a sign of right ventricular hypertrophy. How to Elicit; Place the thenar eminence of the hand over the left side of the sternum, palpating for an abnormal pulsation.Jun 11, 2015 — Clinical features of right heart failure. This was the topic of Question 2 from the second paper of 2015, where 20% of the total mark were attributed to four features of right heart failure. As a disease process typically associated with many concomitant problems and flow-on effects, it is hard to separate the clinical features of right heart .
parasternal heaveJan 27, 2020 — Parasternal heave: Electrocardiographic Findings: Sinus tachycardia Anterior precordial T Wave inversion S1Q3T3 Precordial ST-segment elevation: Echocardiographic Findings: Right heart dilation Septal shift McConnell's sign: RV free wall akinesis sparing the apex: Imaging Findings: Hampton hump: wedge opacity in the .Jan 1, 2018 — A parasternal heave is detected by placing the heel of the hand over the left parasternal region. In the presence of a heave the heel of the hand is lifted off the chest wall with each systole. A parasternal heave is caused by: right ventricular enlargement, or; rarely, severe left atrial enlargement which pushes the right ventricle forwards
The titles featured here from 1950 to 2000 have had a profound effect on American life, but they are by no means the only influential or best ones.
parasternal heave